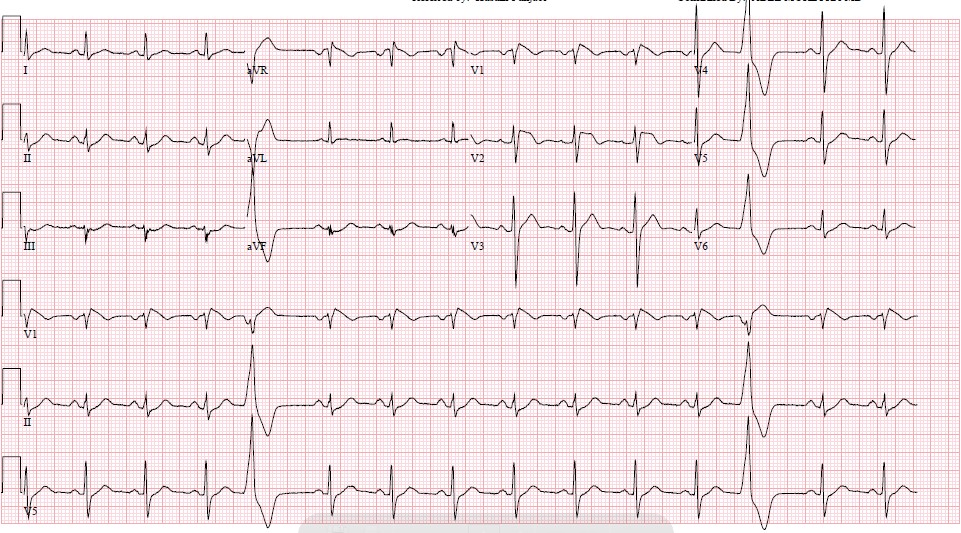
Brugada Type 1 Pattern
Patients with brugada syndrome brs and a spontaneous type 1 ecg are considered to be at greater increased risk for sudden cardiac death than are patients with an abnormal ecg only after administration of sodium channel blockers and therefore represent a more severe phenotype.
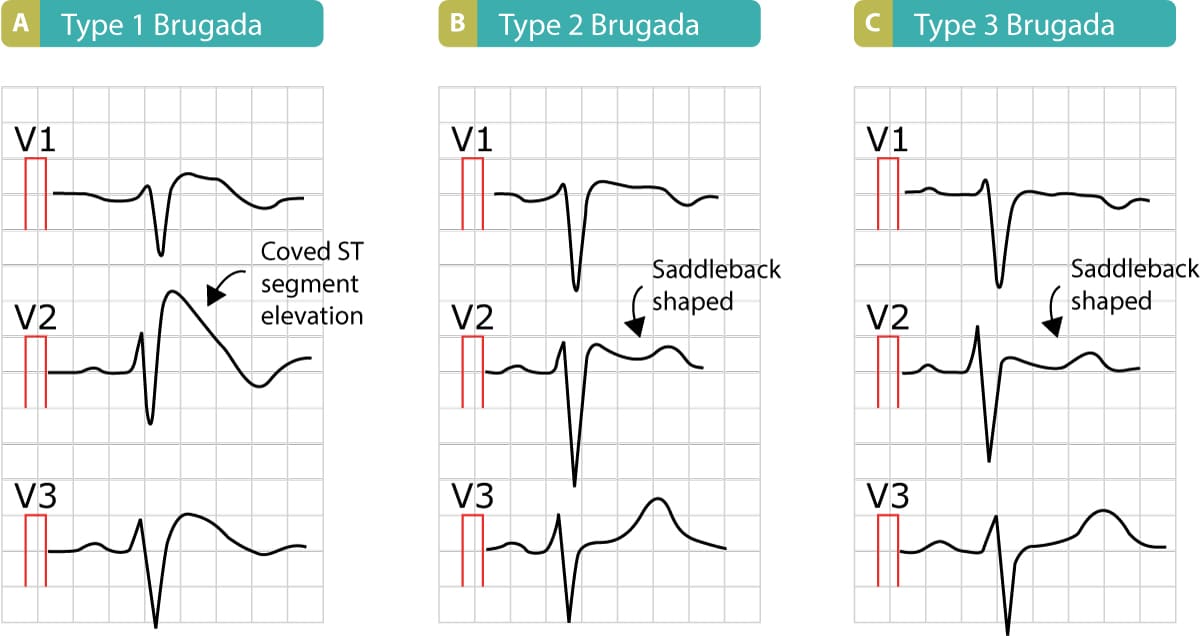
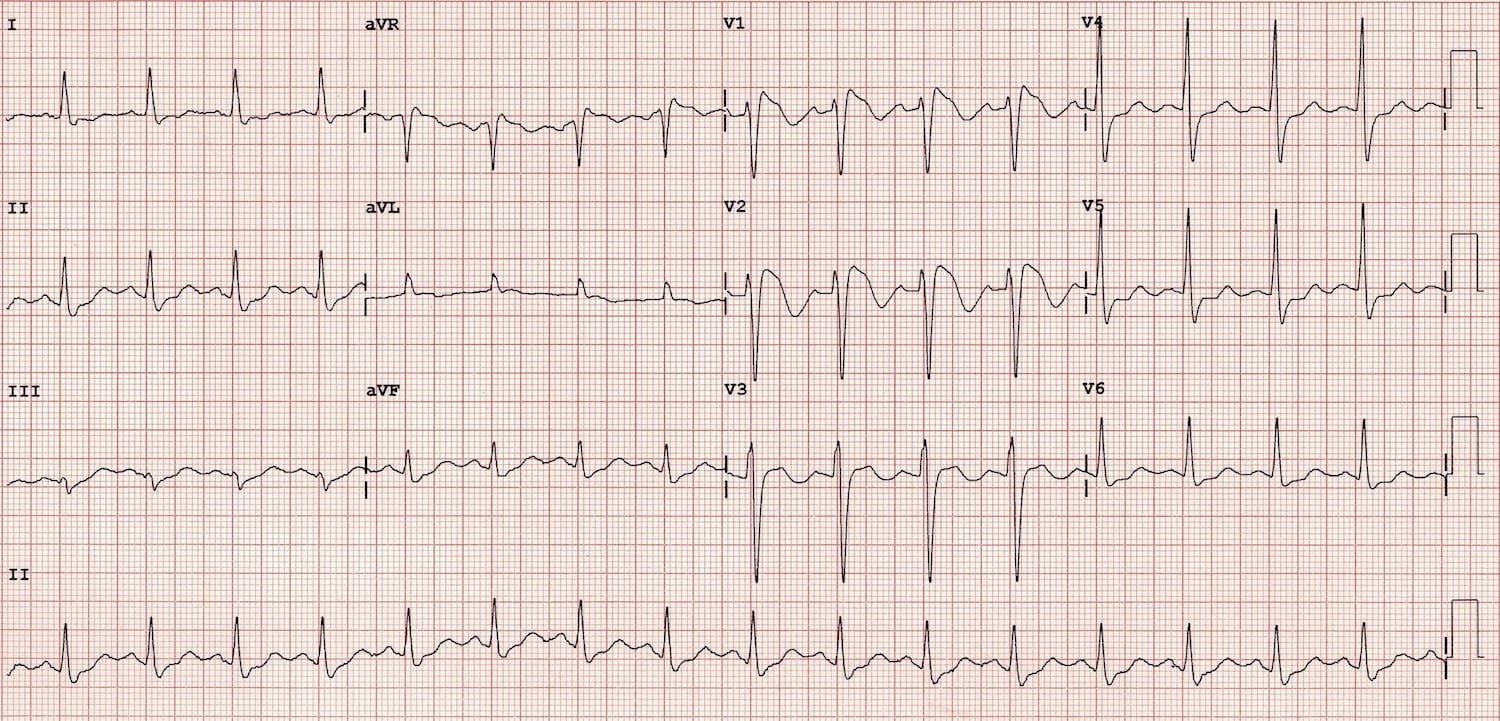
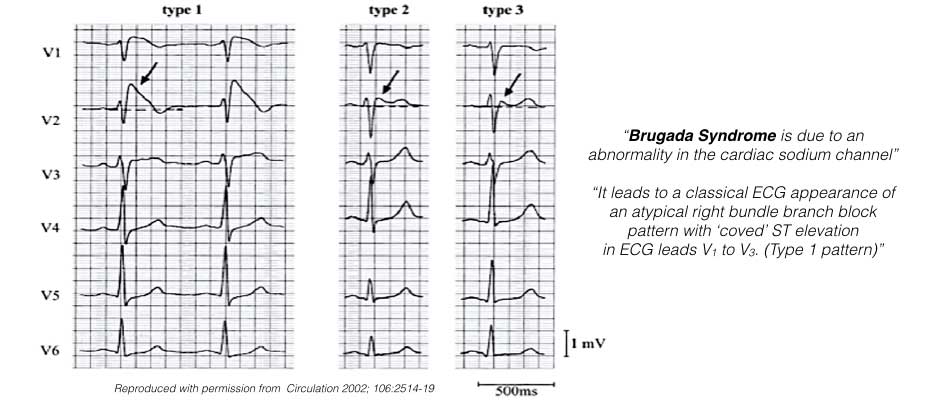
Brugada type 1 pattern. Brugada syndrome is an abnormal ecg right bundle branch block pattern with coved st elevation over the right precordial leads of v1 v3 which leads to ventricular fibrillation vf and sudden cardiac death scd in patients with structurally normal hearts. It is characterised by a prominent coved st segment elevation displaying j point amplitude or st segment elevation 2 mm followed by a negative t wave. The coved st segment elevations may resemble a shark tale. It features large coved st segment elevations and t wave inversions in leads v1 v3.
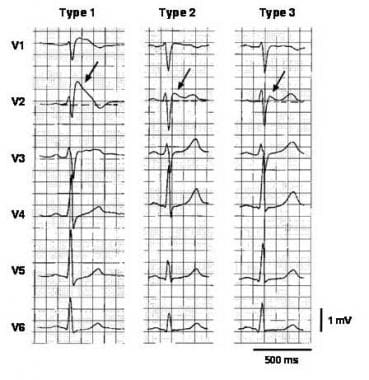
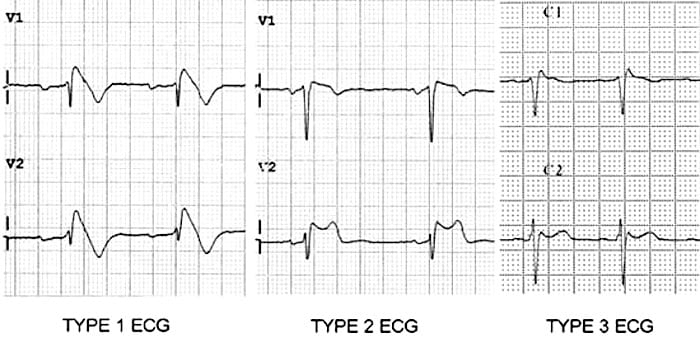
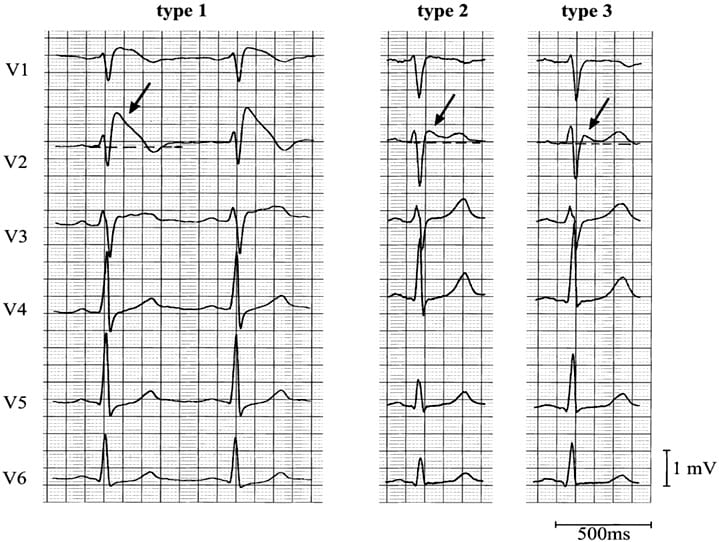
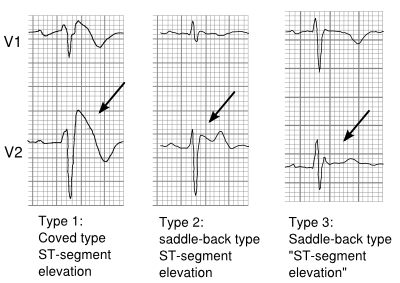
Three forms of the brugada ecg pattern have been described. The brugada syndrome may present with three different ecg patterns referred to as type 1 type 2 and type 2 brugada syndrome ecg. Ekg of brugada syndrome type 1 this pattern was described by brugada brothers in 1992 it is characterized by a prominent coved st segment or j point elevation 2 mm 0 2 mv followed by a negative t wave in at least one right precordial lead v1 or v2 which are placed in a standard or a superior position. Type 1 ekg pattern.
Type 1 has a coved type st elevation with at least 2 mm 0 2 mv j point elevation and a gradually descending st segment followed by a negative t wave. Definition of brugada type 1 pattern the diagnosis of brugada type 1 pattern is based exclusively on the analysis of the electrocardiogram. The panel of experts who elaborated the 2015 esc recommendations on sudden death prevention 1 has reached a consensus on the diagnosis criteria. Brugada type 1 ecg pattern is characterized by a widened terminal r 1st segment elevation and terminal t wave in version that is described as coved type pattern 2.
Type 2 has a saddle back pattern with at least 2 mm j point elevation and at least 1 mm st elevation with a positive or biphasic t wave.